Solidity - Slither
Created by : Mr Dk.
2020 / 02 / 28 18:57
Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
About Slither
是一个 Python 3 实现的 Solidity 静态分析框架。
根据 slither 的 论文,该工具借由 Solidity 编译器产生的 AST,恢复出继承关系图、控制流图等重要信息;并将 Solidity 代码转换为 SSA (Static Single Assessment) 形式的中间表示形式 - SlithIR 。最终,对这种中间表示形式进行代码分析,从而进行威胁检测和代码优化。
SlithIR
为什么需要中间表示形式?
编译器通常可能会将一个程序转换为 AST。然而,编译器可以继续使用各种信息丰富 AST,以便于进行深入的程序分析。比如,Solidity 中有继承机制,这意味着函数可以在当前 contract 源代码以外被定义。IR 可以使这些函数线性化,从而便于对函数执行流进行分析。
类似于 C 语言、LLVM IR、x86 汇编代码。C 语言很明确地进行了函数调用,但缺失了底层系统的细节,比如访问位置的具体信息等;而对于 x86 汇编来说,又缺失了函数调用的传递细节。而 LLVM IR 同时保留了细节信息,因此能够进行深入的程序分析和代码优化。
Variables
状态变量、局部变量、常量等
暂时型变量、引用型变量
Operators
赋值、一元、二元操作符
解引用、取成员操作符
函数调用操作符 (多种)
SSA
这个概念在 LLVM 中也有,但是我暂时还是没有办法理解它的作用。从形式上看,就是将表达式转化为 每个变量只能被赋值一次 的形式。这么做有利于分析,但是具体怎么个有利,以后再深入研究。
Python API
对于上述过程有所了解后,API 的用处就显而易见了。API 接收一个 Solidity 源文件作为输入,并将输入分析为一个 Slither 对象:
from slither.slither import Slither
slither = Slither('file.sol')
首先,通过这个 Slither 对象,可以获得所有的 Contract 对象:
contracts()- 源文件中所有的 contractcontracts_derived()- 源文件中所有非继承 contractget_contract_from_name()- 返回指定名称的 contract
对于每一个 Contract 对象:
name()- 得到 contract 的名称functions()- 得到 contract 中所有的函数 (Function 对象)modifiers()- 得到 contract 中所有的 modifierinheritance()- 所有继承的 contractget_xxx()- 取得 Function 对象、StateVariable 对象等
对于每一个 Function 对象或 Modifier 对象:
name()- 函数名nodes()- 得到函数中所有的 CFG 结点对象 (Node)entry_point()- CFG 的入口结点variables_read()/variables_written()- 被读取或写入的变量列表state_variables_read()/state_variables_written()- 被读取或写入的状态变量列表
对于变量,则有很多不同的类型 - 状态变量、局部变量等,具有属性如变量名、是否被初始化等。
对于 CFG 结点对象 Node,其中包含:
type()- 返回结点的类型expression()- 与该结点相关的表达式 (Expression)- 读取/写入 的 变量/状态变量
而一个 Expression 对象则是一个基于 AST 的代码表示。
基于这些 API,就可以根据不同威胁种类的特定模式,实现对应的检测逻辑。已经内置的代码分析有:
- read/write - 识别对于变量的读写
- protected functions - 只有 contract owner 有权限执行的函数
- data dependency analysis - 对于数据依赖进行的分析 (某个变量是否依赖于另一个变量)
Detectors
检测器使用上述 API 对代码进行分析,从而实现威胁检测或代码优化。目前已经实现了 40 个检测器。
其中每一个检测器的骨架如下:
from slither.detectors.abstract_detector import AbstractDetector, DetectorClassification
class Skeleton(AbstractDetector):
"""
Documentation
"""
ARGUMENT = 'mydetector' # slither will launch the detector with slither.py --detect mydetector
HELP = 'Help printed by slither'
IMPACT = DetectorClassification.HIGH
CONFIDENCE = DetectorClassification.HIGH
WIKI = ''
WIKI_TITLE = ''
WIKI_DESCRIPTION = ''
WIKI_EXPLOIT_SCENARIO = ''
WIKI_RECOMMENDATION = ''
def _detect(self):
info = 'This is an example!'
finding = self.generate_json_result(info)
return [finding]
对于每一种攻击,在 slither 的 WIKI 中阐述了威胁发生的原因与示例的威胁场景。在相应的检测器中,定义了这种威胁的严重程度,和分析这个威胁的信心。
对于每一种威胁,重写 _detect() 函数实现相应的检测逻辑,然后返回一系列的 finding,即 slither 在分析结束后将会打印的信息 (类似编译器的警告信息)。另外还有几个用于辅助的函数,可以将指定的变量 / 结点 / 函数 / contract 加入到最终的 finding 中。Finding 中的信息可以集成到 IDE 里作为代码静态分析的提示。
以 unused_state_variables 为例。这个检测器用于检测 contract 中所有未被使用的状态变量:
"""
Module detecting unused state variables
"""
from slither.detectors.abstract_detector import AbstractDetector, DetectorClassification
from slither.core.solidity_types import ArrayType
from slither.visitors.expression.export_values import ExportValues
from slither.core.variables.state_variable import StateVariable
from slither.formatters.variables.unused_state_variables import format
class UnusedStateVars(AbstractDetector):
"""
Unused state variables detector
"""
ARGUMENT = 'unused-state'
HELP = 'Unused state variables'
IMPACT = DetectorClassification.INFORMATIONAL
CONFIDENCE = DetectorClassification.HIGH
WIKI = 'https://github.com/crytic/slither/wiki/Detector-Documentation#unused-state-variables'
WIKI_TITLE = 'Unused state variables'
WIKI_DESCRIPTION = 'Unused state variable.'
WIKI_EXPLOIT_SCENARIO = ''
WIKI_RECOMMENDATION = 'Remove unused state variables.'
def detect_unused(self, contract):
if contract.is_signature_only():
return None
# Get all the variables read in all the functions and modifiers
all_functions = (contract.all_functions_called + contract.modifiers)
variables_used = [x.state_variables_read for x in all_functions]
variables_used += [x.state_variables_written for x in all_functions if not x.is_constructor_variables]
array_candidates = [x.variables for x in all_functions]
array_candidates = [i for sl in array_candidates for i in sl] + contract.state_variables
array_candidates = [x.type.length for x in array_candidates if isinstance(x.type, ArrayType) and x.type.length]
array_candidates = [ExportValues(x).result() for x in array_candidates]
array_candidates = [i for sl in array_candidates for i in sl]
array_candidates = [v for v in array_candidates if isinstance(v, StateVariable)]
# Flat list
variables_used = [item for sublist in variables_used for item in sublist]
variables_used = list(set(variables_used + array_candidates))
# Return the variables unused that are not public
return [x for x in contract.variables if
x not in variables_used and x.visibility != 'public']
def _detect(self):
""" Detect unused state variables
"""
results = []
for c in self.slither.contracts_derived:
unusedVars = self.detect_unused(c)
if unusedVars:
for var in unusedVars:
info = [var, " is never used in ", c, "\n"]
json = self.generate_result(info)
results.append(json)
return results
@staticmethod
def _format(slither, result):
format(slither, result)
其中,在 _detect() 函数中,调用了 slither 提供的 API,对源文件中的每一个 contract 进行遍历,并调用 detect_unused() 进行检测 - 如果有未被使用的状态变量,则加入到 results 变量中,作为分析结束后的提示。在 detect_unused() 中,收集 contract 中会使用到的所有函数,并提取函数中对变量的读写操作进行分析。如果操作满足特定的模式,就能得出未被使用的状态变量,完成检测。
Example
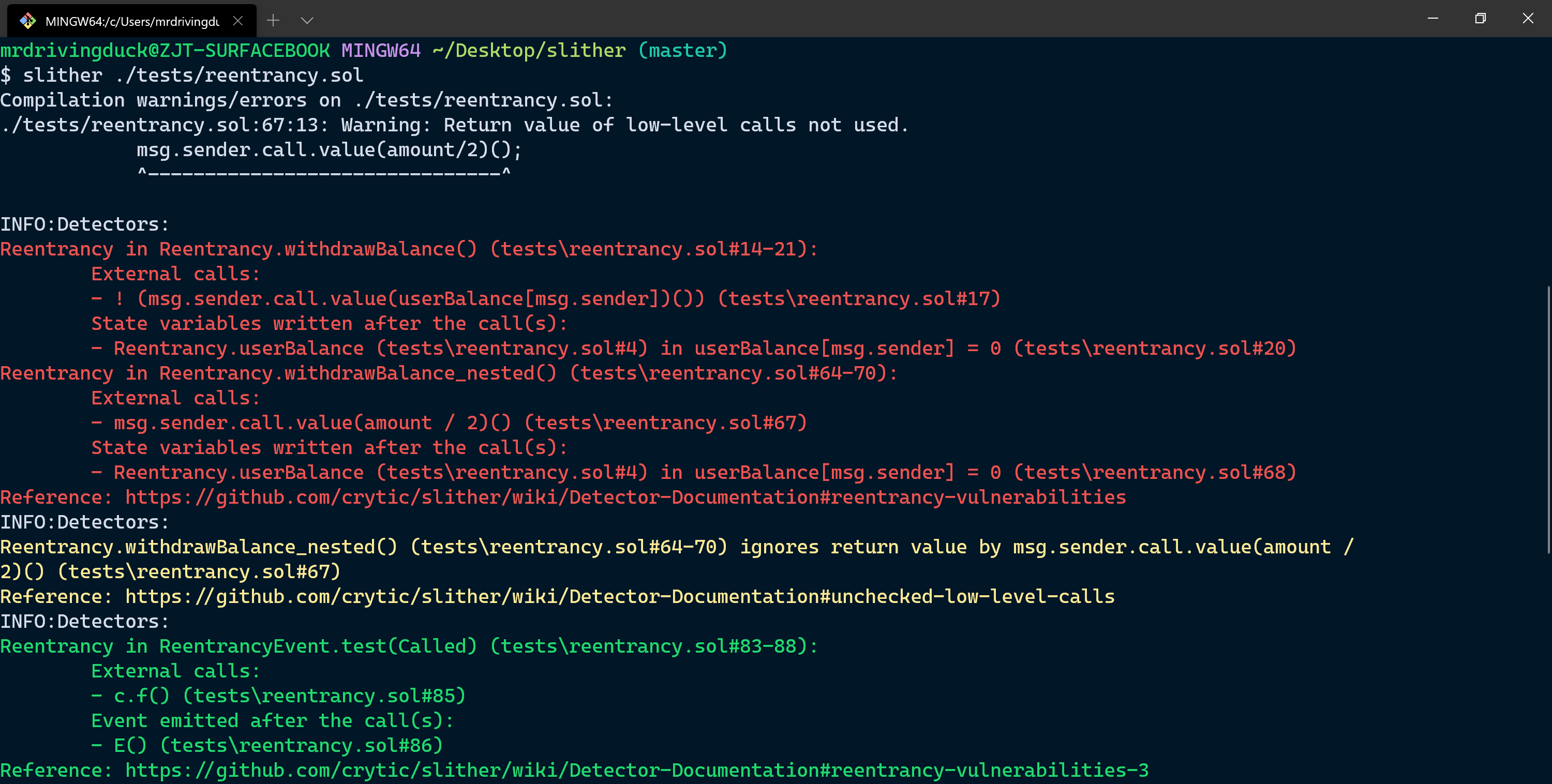
举一个 重入 (Reentrancy) 威胁的例子。想象如下的场景:
function withdrawBalance() public{
// send userBalance[msg.sender] ethers to msg.sender
// if msg.sender is a contract, it will call its fallback function
if( ! (msg.sender.call.value(userBalance[msg.sender])() ) ){
revert();
}
userBalance[msg.sender] = 0;
}
这是一个退款的场景。用户在合约内存有一定的 Ether,想要退款。该合约先将用户在该合约中的余额通过转账退回给用户,然后更新合约中记账的数据结构。然而,当调用转账的函数时,如果用户也是一个 contract,就会触发用户的 fallback function - 在该函数中,恶意用户可能又会调用一次退款函数。此时,由于记账的数据结构还没有更新,合约就会重复退款给用户,以此类推。
检测这种威胁的原则就是,搜索 CFG,在一次外部调用之后,是否出现了对状态变量的写入操作。
Installation && Usage
首先安装 slither 本身:
$ pip3 install slither-analyzer
由于 slither 需要编译器的 AST,因此需要 sloc 编译器。
使用 slither 对一个具有重入威胁的合约进行分析:
Summary
根据 slither 的论文,从三个角度与其它的静态分析工具进行了对比:
- 性能 - 分析是否快速
- 鲁棒性 - 分析是否经常失败
- 准确率 - 分析是否出现误报
在这三个方面,slither 都优于其它的工具。