Chapter 12.9 - block_dev.c 程序
Created by : Mr Dk.
2019 / 09 / 09 20:51
Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
接下来的部分是文件系统的数据访问操作,即系统调用 sys_write() 和 sys_read(),以及不同设备的低层支持函数:
- 访问正规文件:
file_write()/file_read() - 访问管道文件:
pipe_write()/pipe_read() - 访问块设备文件:
block_write()/block_read() - 访问字符设备文件:
rw_char()
在系统调用中,根据参数提供的文件描述符的属性,判断出文件属于哪种类型,分别调用相应的处理函数,并进入对应的驱动程序中。
12.9 block_dev.c 程序
12.9.1 功能描述
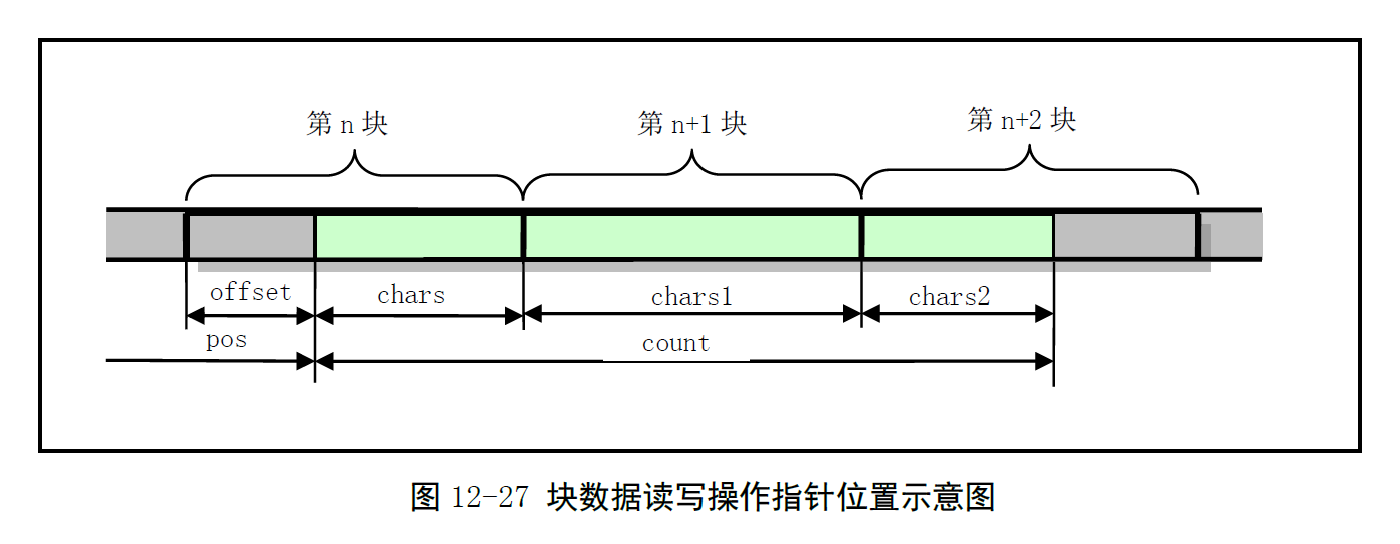
block_read() 和 block_write() 两个函数分别用于读写块设备上的原始数据。由于块设备对磁盘的读写是以盘块为单位的,因此函数中,首先需要把参数中的文件指针映射为 数据块号 和 块内偏移,然后将对应的块读入缓冲区中,并从指定的块内偏移开始处理数据。若还有数据,则继续读取下一块,之后块内偏移总是为 0。原理如图所示:
12.9.2 代码注释
block_write() - 数据块写函数
将 buf 中长度为 count 的数据写到设备 dev 上 pos 开始的位置上。从内核的角度来说,只需要将数据写入缓冲区即可,由块设备驱动程序负责将缓冲区中的数据同步到块设备上。
int block_write(int dev, long * pos, char * buf, int count)
{
int block = *pos >> BLOCK_SIZE_BITS; // pos 所在的数据块号
int offset = *pos & (BLOCK_SIZE - 1); // 块内偏移
int chars;
int written = 0; // 累计写入字节数
int size;
struct buffer_head * bh;
register char * p;
// 设备允许的最大数据块总数
if (blk_size[MAJOR(dev)])
size = blk_size[MAJOR(dev)][MINOR(dev)];
else
size = 0x7fffffff;
// 仍有字节需要被写
while (count > 0) {
// 要写的数据块不能超过设备容许的最大数据块数
if (block >= size)
return written ? written : -EIO;
chars = BLOCK_SIZE - offset; // 本数据块可写入的字节数
if (chars > count)
// 只需要写 count 即可
chars = count;
if (chars == BLOCK_SIZE)
// 恰好需要写一整块,直接申请
bh = getblk(dev, block);
else
// 读入当前块,并预读下两块
bh = breada(dev, block, block + 1, block + 2, -1);
block++; // 下一块
if (!bh)
return written ? written : -EIO;
p = bh->b_data + offset; // p 指向缓冲区中待写位置
offset = 0; // 除了第一块,之后 offset 都为 0
*pos += chars;
written += chars;
count -= chars;
// 从用户空间写入缓冲区
while (chars-- > 0)
*(p++) = get_fs_byte(buf++);
bh->b_dirt = 1;
brelse(bh); // 释放缓冲区
}
return written; // 返回已写入字节数
}
block_read() - 数据块读函数
从设备 dev 的 pos 位置,将 count 字节的数据读入用户缓冲区 buf 中。
int block_read(int dev, unsigned long * pos, char * buf, int count)
{
int block = *pos >> BLOCK_SIZE_BITS; // 数据块号
int offset = *pos & (BLOCK_SIZE - 1); // 块内偏移
int chars;
int size;
int read = 0; // 累积读入字节数
struct buffer_head * bh;
register char * p;
if (blk_size[MAJOR(dev)])
size = blk_size[MAJOR(dev)][MINOR(dev)];
else
size = 0x7fffffff;
// 仍有字节需要读取
while (count > 0) {
if (block >= size)
// 当前读入块号已经大于等于设备上的总块数
return read ? read : -EIO;
chars = BLOCK_SIZE - offset; // 本块中需要读取的字节数
if (chars > count)
// 要读取的字节数不满一块
chars = count;
if (!(bh = breada(dev, block, block + 1, block + 2, -1)))
// 读入需要读取的数据块,并预读后两块
return read ? read : -EIO;
block++;
p = bh->b_data + offset; // p 指向缓冲区读取位置开始处
offset = 0; // 除第一块以外,之后块内偏移都为 0
*pos += chars;
read += chars;
count -= chars;
while (chars-- > 0)
put_fs_byte(*(p++), buf++);
brelse(bh);
}
}