Chapter 10.1-10.2 - HTTP 框架的配置解析与合并
Created by : Mr Dk.
2020 / 07 / 28 20:08
Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
10.1 HTTP 框架概述
在 Nginx 中,HTTP 框架是事件消费模块的大户。HTTP 框架要完成的基础性工作包含:
- 处理
http{}块内的配置项 - 监听 Web 端口,处理新连接事件、可读事件、可写事件
- 通过状态机,分析接收到的 TCP 字符流是否是完成的 HTTP packet
- 根据接收到的 HTTP 请求的 URI 和 HTTP header,按请求所在阶段,分发到某个 HTTP 模块,调用其回调函数处理请求
- 向 HTTP 模块提供必要的工具函数 (处理网络 I/O 和磁盘 I/O)
- 提供 upstream 机制帮助 HTTP 模块访问第三方服务
- 提供 subrequest 机制帮助 HTTP 模块实现子请求
一个典型的 HTTP 配置:
http {
...;
server {
...;
location /L1 {
...;
}
location /L2 {
...;
}
}
server {
...;
location /L1 {
...;
}
location /L2 {
...;
}
}
}
可以看到,HTTP 框架支持在一个 http{} 块中包含多个 server{} 块和多个 location{} 块。ngx_http_module 核心模块定义了新的模块类型 NGX_HTTP_MODULE。这类模块中的 ctx 被定义为 ngx_http_module_t,是所有 HTTP 模块的通用接口。ngx_http_module_t 接口完全围绕着解析配置项来进行。其中包含三类配置项:
- 直接隶属于
http{}块的 main 配置项 - 直接隶属于
server{}块的 srv 配置项 - 直接隶属于
location{}块的 loc 配置项
typedef struct {
// 解析 http{} 块前后的回调
ngx_int_t (*preconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
ngx_int_t (*postconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
// 创建存储 http{} 中配置项的结构体
void *(*create_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
// 解析完 http{} 内 main 配置项的回调
char *(*init_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *conf);
// 创建存储 server{} 中 srv 配置项的结构体
void *(*create_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
// 将 main 中的配置项合并到 srv 中
char *(*merge_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
// 创建存储 location{} 中 loc 配置项的结构体
void *(*create_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
// 将 main、srv 中的配置项合并到 loc 中
char *(*merge_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
} ngx_http_module_t;
10.2 管理 HTTP 模块的配置项
HTTP 模块配置项的复杂性。HTTP 模块有三种等级的配置项,对于 HTTP 模块而言,只需要关心在工作时能够正确取到配置项即可。但对于 HTTP 框架来说,其 server 相关的配置项可能会出现在 main 级别中,location 相关的配置项可能会出现在 main、srv 级别中。所以在解析完配置项后,还要进行 合并 操作,把 main 级别、srv 级别的配置项合并到 loc 级别配置项中。具体的合并行为也可以通过实现 ngx_http_module_t 中的 merge() 函数自行定义行为。
具体涉及到数据结构的组织非常复杂。在 CSDN 上盗了个图,不想贴代码了:
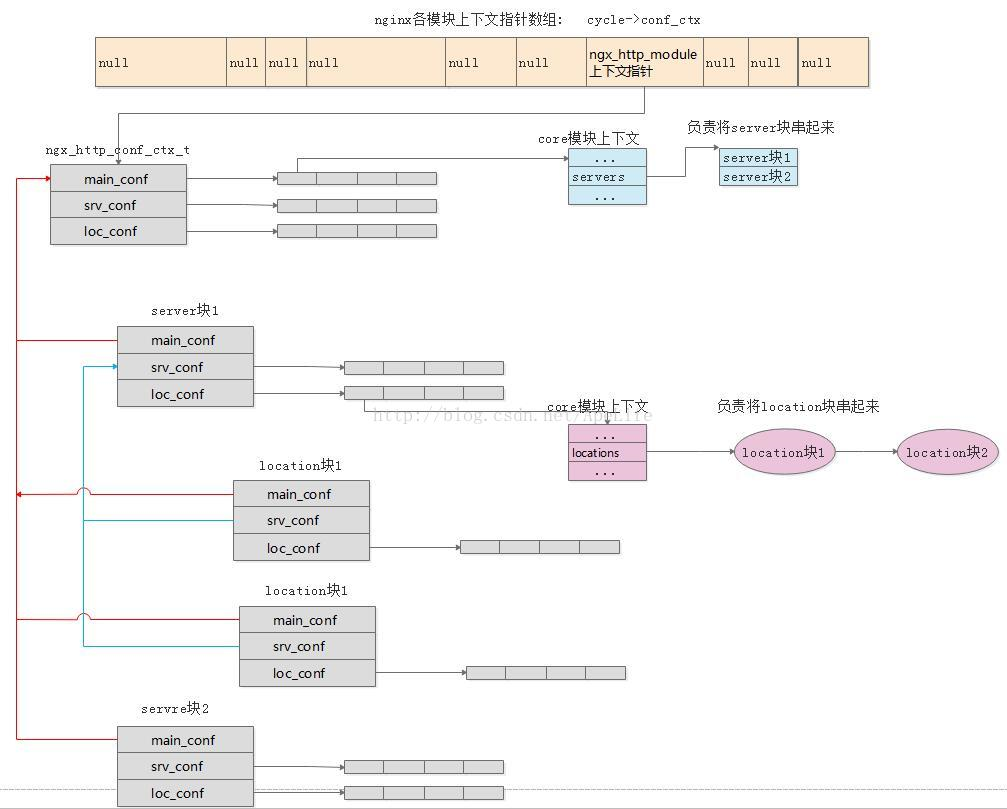
首先是存储配置项的结构体定义。这个结构体会被 每一个 HTTP 模块 解析 每一个等级的配置项 时建立:
typedef struct {
void **main_conf;
void **srv_conf;
void **loc_conf;
} ngx_http_conf_ctx_t;
在解析到 http{} 块的 main 级别配置项时,会分别调用每个 HTTP 模块的 create_main_conf()、create_srv_conf()、create_loc_conf() 函数,通过这个结构体,建立属于 http{} 块的配置项。
在解析到 server{} 块时,则回调 ngx_http_core_server(),开始解析 srv 级别的配置项。同样也会建立属于这个 server{} 块的 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体。其中,main_conf 指针指向所属 http{} 块的 main_conf,而 srv_conf 和 loc_conf 都会重新分配数组,并依次调用所有 HTTP 模块的 create_srv_conf() 函数和 create_loc_conf() 函数。
在解析到 location{} 块时,回调 ngx_http_core_location(),开始解析 loc 级别的配置项。同样这里也会建立属于 location{} 块的 ngx_http_conf_ctx_t 结构体,其中 main_conf 和 srv_conf 分别指向所属 server{} 块的 main_conf 和 srv_conf。而 loc_conf 则将会重新分配指针数组,并依次调用所有 HTTP 模块的 create_loc_conf() 函数。
可以看到,create_loc_conf() 被三个等级的配置项分别调用了一次,它们都可以被合并到 loc 级别的配置中;create_srv_conf() 被两个等级的配置项分别调用了一次,它们都可以被合并到 srv 级别的配置中。
首先进行的是 main 级别与 srv 级别的同名配置的合并 (节选自 ngx_http_block() 函数):
/*
* init http{} main_conf's, merge the server{}s' srv_conf's
* and its location{}s' loc_conf's
*/
cmcf = ctx->main_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
cscfp = cmcf->servers.elts;
// 遍历所有 Nginx 模块
for (m = 0; cf->cycle->modules[m]; m++) {
// HTTP 类型的模块
if (cf->cycle->modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) {
continue;
}
// 获得模块结构体和编号
module = cf->cycle->modules[m]->ctx;
mi = cf->cycle->modules[m]->ctx_index;
/* init http{} main_conf's */
if (module->init_main_conf) {
rv = module->init_main_conf(cf, ctx->main_conf[mi]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
}
// 将 http{} 块中的配置向 server{} 块中合并
rv = ngx_http_merge_servers(cf, cmcf, module, mi);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
}
ngx_http_merge_servers() 函数中,将 http{} 块对应的配置结构体中的 srv_conf 和 loc_conf 合并到 server{} 块的 srv_conf 和 loc_conf 中。
static char *
ngx_http_merge_servers(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf,
ngx_http_module_t *module, ngx_uint_t ctx_index)
{
char *rv;
ngx_uint_t s;
ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx, saved;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t **cscfp;
cscfp = cmcf->servers.elts; // 所有 server{} 块下的配置
ctx = (ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *) cf->ctx; // http{} 块下的全局配置
saved = *ctx;
rv = NGX_CONF_OK;
// 遍历所有 server 块下的 srv 级别配置
for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
/* merge the server{}s' srv_conf's */
ctx->srv_conf = cscfp[s]->ctx->srv_conf;
// 如果当前 HTTP 模块实现了 http{} 块到 server{} 块的 srv 级别配置的合并函数
if (module->merge_srv_conf) {
// 调用合并函数,参数分别为 http{} 块的 srv 配置和 server{} 块的 srv 配置
rv = module->merge_srv_conf(cf, saved.srv_conf[ctx_index],
cscfp[s]->ctx->srv_conf[ctx_index]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
}
// 如果当前 HTTP 模块实现了 http{} 块到 server{} 块的 loc 级别配置的合并函数
if (module->merge_loc_conf) {
/* merge the server{}'s loc_conf */
ctx->loc_conf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf;
// 调用合并函数,参数分别为 http{} 块的 loc 配置和 server{} 块的 loc 配置
rv = module->merge_loc_conf(cf, saved.loc_conf[ctx_index],
cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ctx_index]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
/* merge the locations{}' loc_conf's */
clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
// 开始将 server{} 块中的配置向 location{} 块中合并
rv = ngx_http_merge_locations(cf, clcf->locations,
cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf,
module, ctx_index);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
}
}
failed:
*ctx = saved;
return rv;
}
在 ngx_http_merge_locations() 函数中,将 server{} 块的 loc_conf (此时已经与 http{} 块的 loc_conf 合并) 与 location{} 块的 loc_conf 合并:
static char *
ngx_http_merge_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
void **loc_conf, ngx_http_module_t *module, ngx_uint_t ctx_index)
{
char *rv;
ngx_queue_t *q;
ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx, saved;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
ngx_http_location_queue_t *lq;
// 当前 server 块下没有 location 块,直接返回
if (locations == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}
ctx = (ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *) cf->ctx;
saved = *ctx;
// 遍历每一个 location 块
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
ctx->loc_conf = clcf->loc_conf;
// 合并 server{} 块与 location{} 块的配置项
rv = module->merge_loc_conf(cf, loc_conf[ctx_index],
clcf->loc_conf[ctx_index]);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
// location 块可以嵌套 location 块,所以递归
rv = ngx_http_merge_locations(cf, clcf->locations, clcf->loc_conf,
module, ctx_index);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
return rv;
}
}
*ctx = saved;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}