4 - Channel Concept
Created by : Mr Dk.
2021 / 02 / 19 13:10
Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Channel
Channel 表示可被 I/O 操作的组件的抽象表示,可以被读取 / 写入 / 连接 / 绑定。典型的例子:socket。Channel 可以向用户提供如下信息:
- 当前
Channel的状态 (已打开 / 已连接?) Channel的配置参数 (接收缓冲区大小)Channel支持的 I/O 操作- 处理
Channel的 I/O 事件及请求的ChannelPipeline
在 Netty 中,所有的 I/O 操作都是异步的,返回值不保证 I/O 操作是否成功。返回的 ChannelFuture 实例能够在 I/O 操作成功 / 失败 / 取消时通知用户。
Channel 可以是层次化的,由具体的传输实现决定。一个 channel 可以有一个 parent(),比如,一个由 ServerSocketChannel 接受的 SocketChannel 将会在调用 parent() 时返回 ServerSocketChannel。
Channel 应在使用完毕后被关闭,以释放资源。
ChannelHandler
用于 截获 并 处理 I/O 事件,并向 ChannelPipeline 中的下一个 ChannelHandler 转发事件。每个 ChannelHandler 都由一个 ChannelHandlerContext 提供,通过该对象,ChannelHandler 可以与 ChannelPipeline 进行交互,以便传递事件,或动态修改流水线 (编排 ChannelHandler)。
如果 ChannelHandler 类内维护了状态变量,为了避免竞争条件,用户需要为每一个 Channel 对应的 ChannelPipeline 分配独立的 ChannelHandler 实例。理论上,相同的 ChannelHandler 实例可以被共享,添加到不同的 ChannelHandler 上。
根据 ChannelHandler 的功能不同,该接口派生出了如下子接口:
ChannelInboundHandler- 处理入站 I/O 事件ChannelOutboundHandler- 处理出站 I/O 事件ChannelDuplexHandler- 同时处理双向 I/O 事件
对于前两种接口,Netty 已经提供了默认实现类,用户只需要继承默认实现类并重写自己想要定制的函数即可:
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapterChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter
ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline 由拦截流经 Channel 的出入站事件的 ChannelHandler 实例链组成。每个新创建的 Channel 都会被分配一个新的 ChannelPipeline,这个关联是永久性的,它们之间的绑定不会分离。ChannelPipeline 提供 API 能够实时修改内部 ChannelHandler 的布局 (添加 / 删除 / 替换),从而实现动态协议切换。
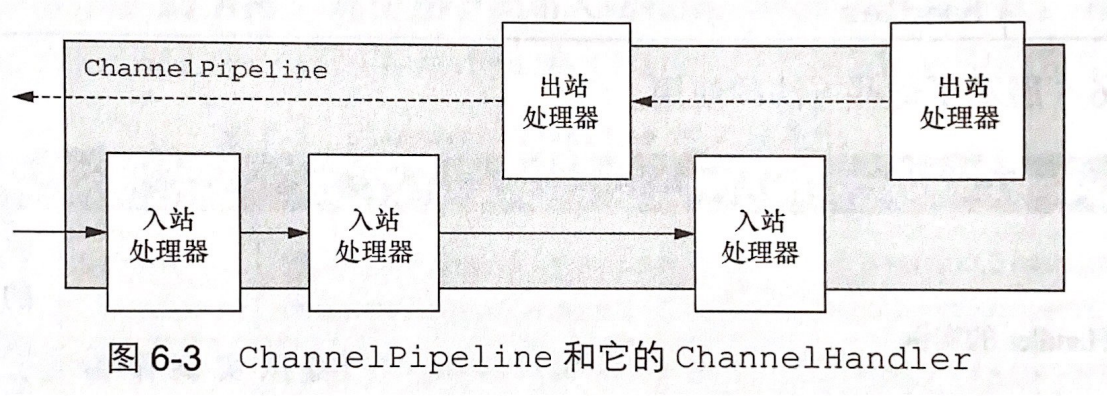
通常 ChannelHandler 的代码都是由 EventLoop 线程来执行的,因此至关重要的一点是不要在 ChannelHandler 中阻塞当前线程。如果不得不调用阻塞 API,ChannelPipeline 提供了接受 EventExecutorGroup 的 add() API,使得该 ChannelHandler 会在提供的 EventExecutorGroup 中被处理,而不是使用当前的 EventLoop 线程执行。
ChannelHandlerContext
ChannelHandlerContext 代表了 ChannelHandler 和 ChannelHandlerPipeline 之间的关联。当 ChannelHandler 被添加到流水线上时,就会创建一个 ChannelHandlerContext 实例。其主要功能是管理其连接的 ChannelHandler 与流水线上其它 ChannelHandler 之间的交互。
由于一个 ChannelHandler 实例可以从属于多个 ChannelPipeline,因此可以同时绑定到多个 ChannelHandlerContext 中。此时,ChannelHandler 必须使用 @Sharable 注解标注,否则将触发异常。被共享的 ChannelHandler 必须是线程安全的。
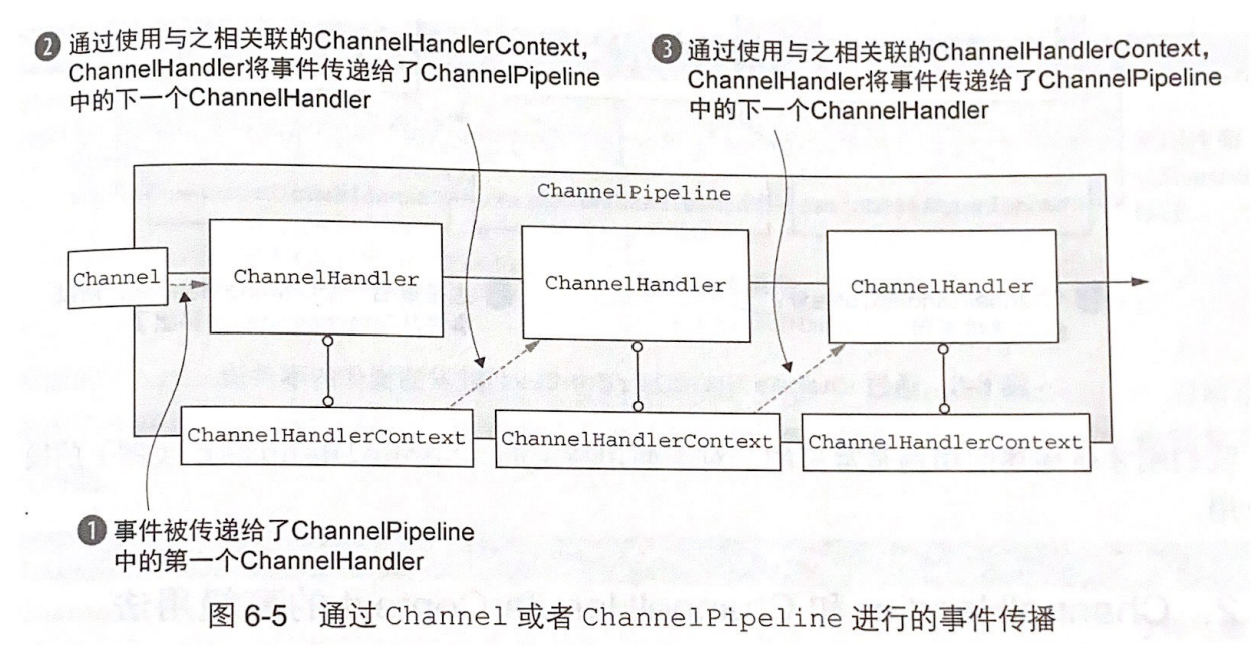
该接口上定义的函数很多也存在与 Channel 与 ChannelPipeline 中,但不同的是,调用 ChannelHandlerContext 上的函数将使操作从当前的 ChannelHandler 开始向后传播给能够处理该事件的 ChannelHandler;而 Channel 或 ChannelPipeline 上的操作将沿整个 ChannelPipeline 传播。从而减少事件流经对它不感兴趣的 ChannelHandler 带来的开销。